Category: Oil and Gas
Aksa Natural Gas Distribution
Istanbul, Turkey
Category: Oil and Gas
Istanbul, Turkey
“What previously would have taken two hours with the older system to configure within one RMS system now takes 10 seconds within GENESIS.”
Aksa Natural Gas Distribution, Inc. (www.aksadogalgaz.com.tr), headquartered in Istanbul, Turkey, is a natural gas distributor subsidiary of Kazanci Holding, operator of multiple power generation, natural gas distribution, energy generation, and electricity distribution and sales companies throughout Turkey. Aksa operates its natural gas distribution and retail sales activities in 214 districts within 27 Turkish provinces. By the end of 2021, the company increased its total network size to over 34,000 kilometers, its subscriber number to over 4 million, and provided over 11 billion cubic meters of gas distribution.
“What previously would have taken two hours with the older system to configure within one RMS system now takes 10 seconds within GENESIS.”
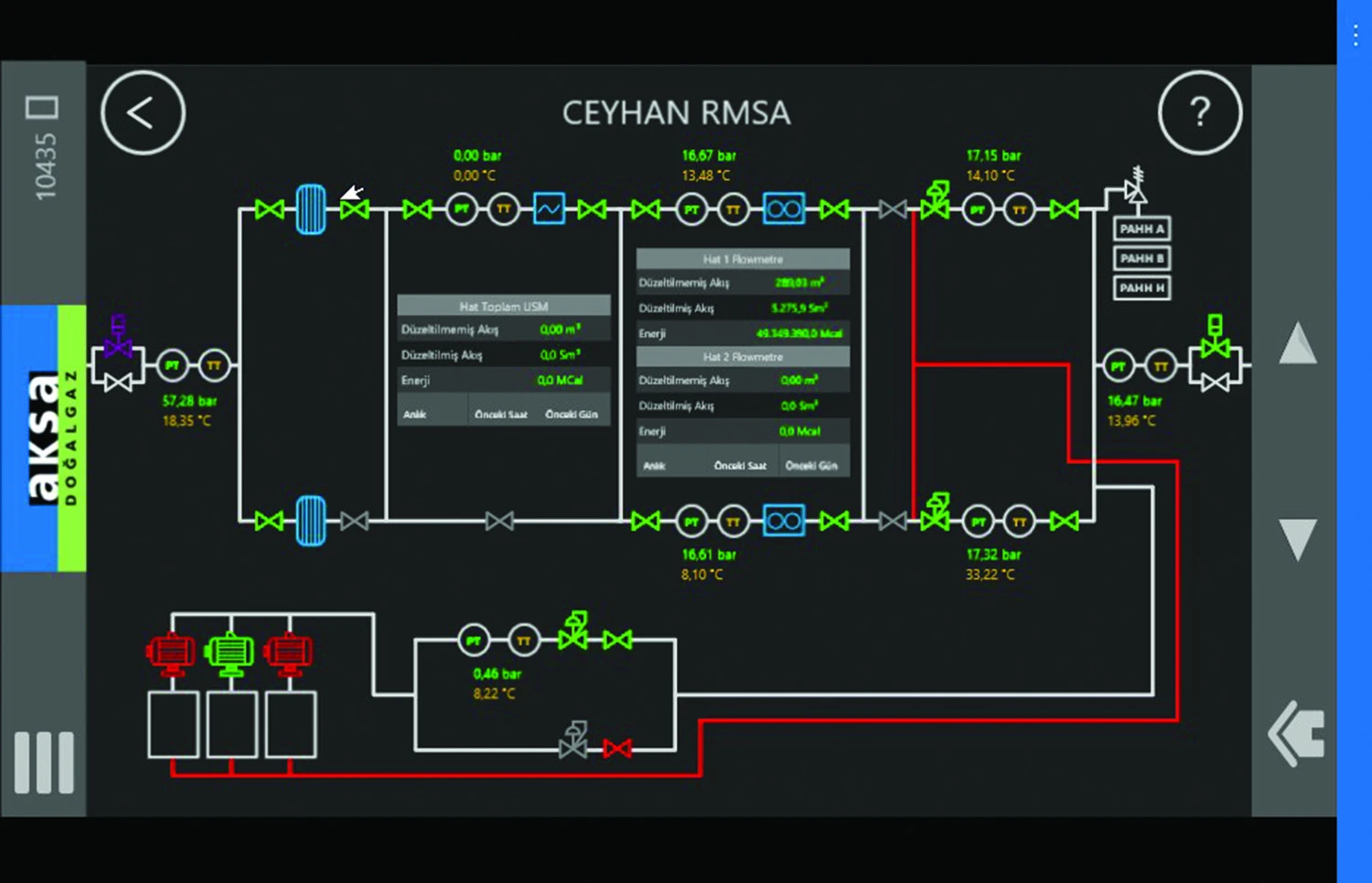
 An Aksa Natural Gas Chart Display for Mobile Devices through MobileHMI
An Aksa Natural Gas Chart Display for Mobile Devices through MobileHMI
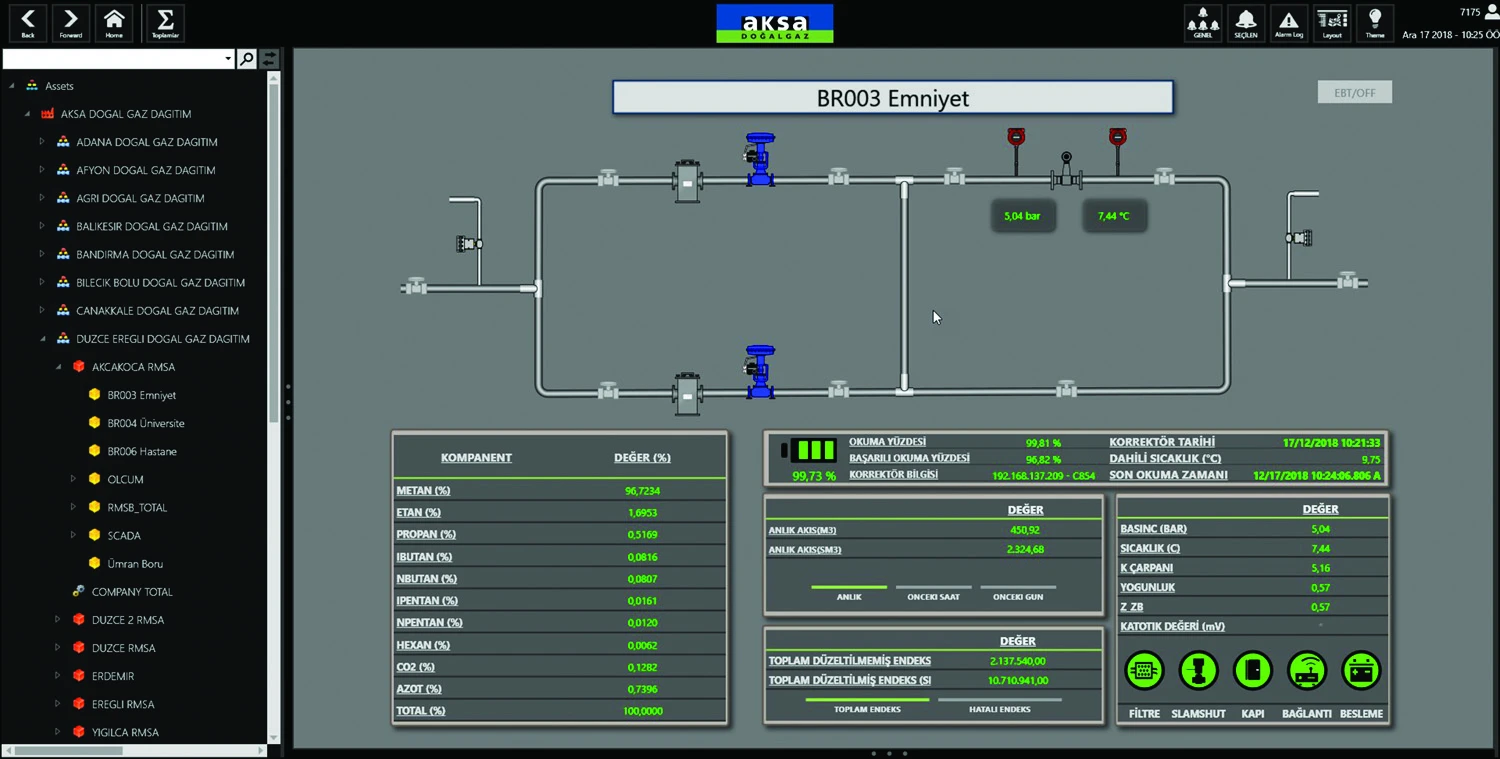
Aksa sought an automation system for its Natural Gas Regulating and Metering Stations (RMSs), divided into three separate types (A, B, C) according to pressure classes. RMSs reduce and regulate downstream pressure, measuring the quantity of energy transferred from Aksa’s natural gas transmission system to medium pressure networks or to consumers who are connected directly to the transmission system. They also add the distinctive odor to the gas, providing prompt detection of any leakages, as required by national and international safety standards. An RMS can consist of one or more sections and systems depending on the application. These can include inlet valves, filtering, pre-heating, pressure regulating, metering, outlet valves, odorizing, gas quality measurement, flow computer/invoicing, and/or PLC-based control/supervision.
Aksa requires station data (in digital or analog values) to be gathered by a central HMI/SCADA system via OPC servers and PLCs. Alarms are generated from critical values within the received data. For example, station outlet pressure needs to be around 15 bar. Anything above or below this value could cause problems. Aksa required that their selected alarm management system be able to integrate with their RMS system, as well as provide notifications (through email, etc.). The alarm management system needed to handle thousands of tags, with each tag status made available to multiple locations, and if necessary, allow for expected intervention within 15 minutes. Each of Aksa’s 120 RM/A (type A) station contains a local HMI/SCADA display. Operators work in three shifts to monitor screens to check the accuracy of alarms and consumption information.
The quality of natural gas changes constantly. Therefore, RM/A stations have gas chromatograph devices that measure the quality of the gas every four to five minutes. As chromatograph devices are typically very expensive, they are not located at Aksa’s 1,400 RM/B or RM/C stations. Therefore, monthly fixed values are entered via Electronic Volume Correctors (EVC). Aksa wanted to ensure that their new HMI/SCADA system could write these values to their 1,400 EVCs that perform this measurement at their RM/B and RM/C stations, thus helping to increase their accuracy.
 An Aksa Natural Gas Chart Display for Mobile Devices through MobileHMI
An Aksa Natural Gas Chart Display for Mobile Devices through MobileHMI
 An Aksa Regulating/Metering Station Display Configured for Mobile Device Use
An Aksa Regulating/Metering Station Display Configured for Mobile Device Use
Aksa Natural Gas Distribution, Inc. selected GENESIS HMI/SCADA suite (including GraphWorX64 advanced visualization), Hyper Historian rapid data historian, AlarmWorX64 Multimedia alarm management system, MobileHMI data mobility suite, and KPIWorX self-service real-time dashboard tool.
Aksa ultimately decided upon GENESIS for its automation software needs for several reasons. The company appreciated that GENESIS and its additional tools could help reduce engineering time for their applications. They also wanted to utilize the geographical information system (GIS) integration, connecting to assets within map-based displays. Aksa was also pleased with the variety of data access methods, whether through web interface on desktops and laptops or through “any glass”, taking advantage of the mobile device integration through MobileHMI and KPIWorX.
 An Aksa Regulating/Metering Station Display Configured for Mobile Device Use
An Aksa Regulating/Metering Station Display Configured for Mobile Device Use
The natural gas distributor is now able to remotely monitor and measure data throughout its extensive distribution network, which contains over 120,000 active tags. GENESIS interfaces with multiple pieces of equipment including Fatek and Motorola Moscad PLCs. As data is transmitted to the central data system, equipment properties are collected into an asset tree, created in Aksa’s preferred hierarchy for use by its operators. Aksa also connects GENESIS64 to its Oracle database (used by its own GIS department to calculate the amount of gas throughout its pipelines), as well as to Microsoft SQL Server (to view consumption data written from local systems to a SQL table), to multiple Windows Server 2012 R2 machines, and to its KEPServerEX Connectivity Platform.
What previously would have taken two hours with the older system to configure within one RMS system now takes 10 seconds within GENESIS. Aksa now benefits from the capability to share newly configured stations with users via quick web deployment and from instant visibility of any changes made.
Aksa continues to utilize the GENESIS platform throughout its natural gas distribution network. GENESIS has helped save the company development and operations time and costs. The company plans to expand its use of these solutions in the future, which includes greater utilization of the Reporting module to automatically extract invoices from all screens, as well as expand its use of GENESIS by performing real-time latitude/longitude calculations to help direct technician and emergency teams during malfunctions. The company also plans to eventually utilize three-dimensional display configurations for its multiple stations.